WAF CQRS Pattern
August 12, 2025•276 words•2 min read•
azure
design patterns
performance efficiency
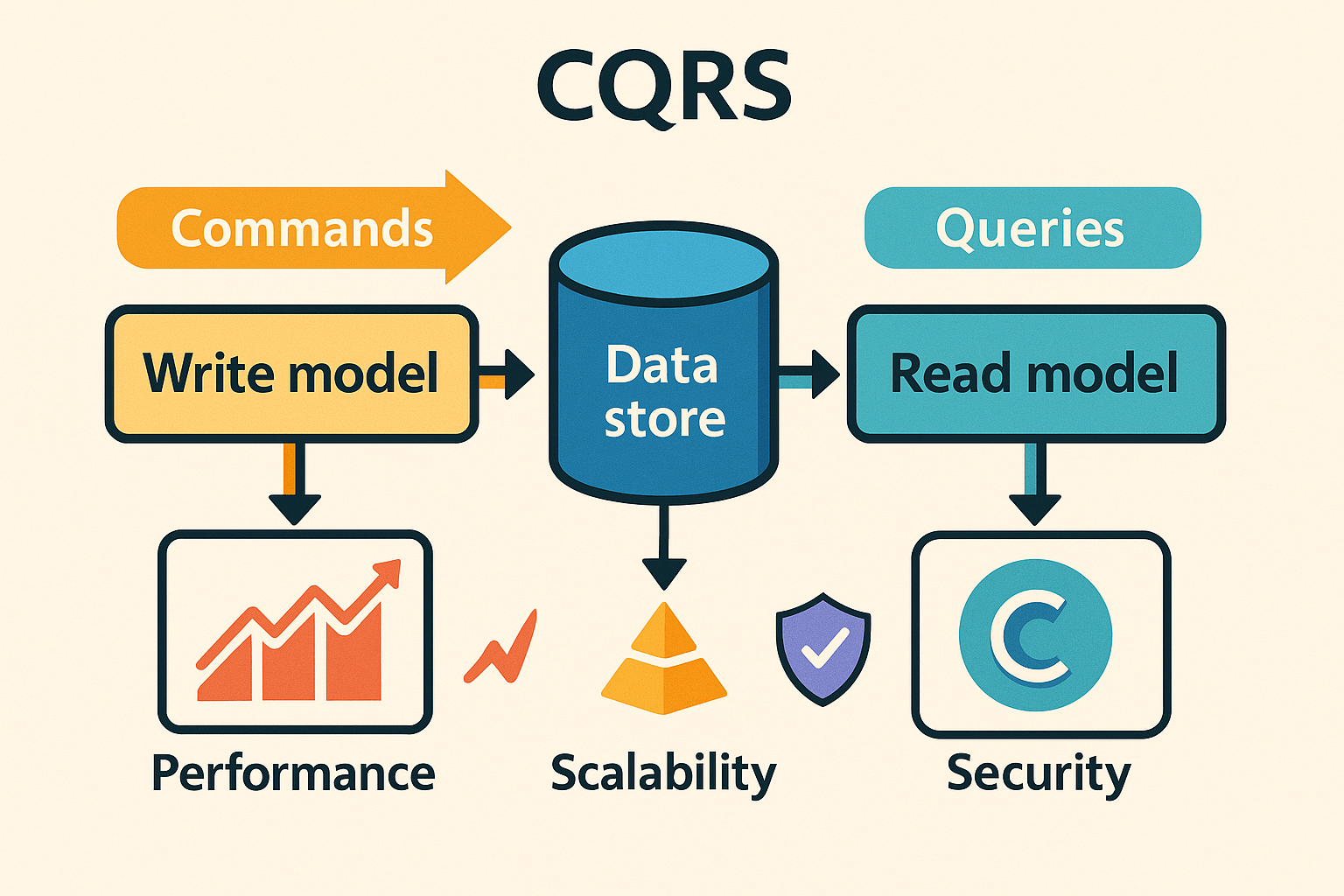
| Category | Description | WAF Description |
|---|---|---|
| What | Separates the models for handling commands (writes that change state) and queries (reads that fetch data), allowing each to evolve independently. | Boosts performance and scalability by optimizing read and write paths separately, and supports security by isolating operations based on their purpose and responsibilities. |
| Used with | Systems where reads and writes have differing workload profiles—such as high read-load apps, event-driven designs, or when using materialized views. | Enhances operational excellence and performance efficiency by allowing each model to scale and be maintained independently, reducing coupling and improving resource utilization. |
| When | When read and write workloads diverge in complexity or scale, or when you need to optimize for query performance without compromising write integrity. | Aligns with reliability and performance pillars by reducing lock contention, enabling tailored scaling strategies, and simplifying model evolution for specific concerns. |
| Not Suitable For | Simple CRUD applications where separation adds unnecessary complexity and overhead, or when immediate consistency is critical across data operations. | Could hinder operational excellence and cost optimization in low-complexity scenarios due to added architectural complexity and potential delays from eventual consistency. |
| Related To | Materialized View, Event Sourcing, Domain-Driven Design (DDD), Event-Driven Architecture, Distributed Transactions. | Event Sourcing Pattern, Materialized View Pattern |
A basic implementation of the Command Query Responsibility Segregation (CQRS) Pattern can be found here.
The full WAF description of the pattern can be found here.